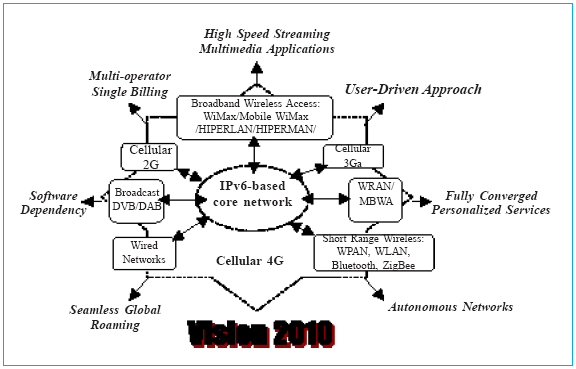
Fig 1 4G vision 2010
| 254 | IETE TECHNICAL REVIEW, Vol 23, No 4, 2006 |
This era marked the beginning of full-fledged huge revenue generating
multimedia Internet applications and e-commerce. b. Migration to the Future These limitations and drawbacks have generated the requirement for an universal framework encompassing all the existing heterogeneous wired and wireless systems in use. This IPv6-based potential 4G framework, commonly described as MAGIC [3] (Mobile multimedia, Anytime anywhere access, Global mobility support, Integrated wireless solution and Customized personal service), would be highly |
dynamic and significantly handle the limitations of 3G systems. So, consolidated solutions that can seamlessly operate on the multiple, diverse networks migrating to the 4G environment fulfilling the plethora of nextgeneration dream visualizations on implementing a transparent open wireless architecture (OWA), should be imperatively designed. This obviously invites new challenges on every step and researchers worldwide face an uphill task of designing suitable solutions. Figure 1, shows such a 4G vision. This paper is divided into four sections:
introduction, overview of the potential research
challenges, highlighted research challenges and
conclusions. We have identified a whole lot of probable
4G research challenges and have grouped them under 2.OVERVIEW OF THE POTENTIAL RESEARCH CHALLENGES The different potential challenges are summarized in Table 1. Section 3 discusses in details on few of the highlighted research challenge areas. Table 2 represents the abbreviation used in this article.
|

Fig 1 4G vision 2010